Operating System
OS Part-1
OS Part-2
- File Concepts and Access methods
- Free Space Management and Allocation methods
- Directory Systems and Protection
- File Organization, Sharing and Implementation issues
- Disk and Drum Scheduling
- I/O Devices Organisation & I/O Buffering
- I/O Hardware, Kernel I/O subsystem and Transforming I/O Requests to Hardware Operations
- Device Drivers and Path Management
- Device Driver Sub Modules and Procedure
- Device Scheduler and Handler
- Interrupt Service Routine (ISR)
- File System in Linux and Windows
OS Part-3
- Process and Process Control Block(PCB)
- Process Scheduling( Preemptive and Non Preemptive)
- Scheduling Algorithms
- Algorithm Evaluation
- Multiple Processor Scheduling
- Real Time Scheduling
- Operations on Processes
- Threads
- Inter-Process Communication
- Precedence Graphs
- Critical Section Problem
- Semaphores
- Classical Problems of Synchronization
- DeadLock
- Deadlock Prevention and Avoidance
- Deadlock Detection and Recovery
- Process Management in Linux
OS Part-4
- Memory Hierarchy in OS
- Concepts of Memory Management
- MFT and MVT
- Logical and Physical Address Space
- Swapping
- Contiguous and Non Contiguous Memory Allocation
- Paging
- Segmentation
- Paging Combined with Segmentation
- Structure and Implementation of Page Table
- Virtual Memory in OS
- Cache Memory Organization
- Demand Paging
- Page Replacement Algorithms
- Allocation of Frames and Thrashing
- Demand Segmentation
OS Part-5
- Distributed Operating System: Introduction and Types
- Distributed OS: Design Issues
- Distributed OS: File System
- Distributed OS: Remote File Access
- Remote Procedure Call(RPC)
- Remote Method Invocation(RMI)
- Distributed Shared Memory
- Parallel Processing and Concurrent Programming
- Security and Threats Protection in Distributed OS
- Security Design Principles and Authentication in Distributed OS
- Sensor Network and Parallel OS
Process in Operating System – Concept & Process Control Block
Process kya hota hai?
Process ek running program hota hai. Jab koi program execute hone lagta hai, to wo ek process ban jata hai.
Example:
Jab aap MS Word open karte ho, to wo ek process ban jata hai jo system pe run ho raha hota hai.
Agar aap do alag-alag Word documents open karte ho, to dono alag processes hongi, chahe program same ho.
Process ke Components:
1. Program Code – Jisme actual instructions hoti hain.
2. Data – Input aur output values jo process use karega.
3. Process Stack – Temporary data jaise function calls aur local variables store karta hai.
4. Heap – Dynamically allocated memory rakhta hai.
5. Registers – CPU ke registers jo process ki information rakhte hain.
6. Program Counter (PC) – Next instruction ka address store karta hai jo execute hone wala hai.
Process States in OS
Ek process apni execution ke dauraan alag-alag states se guzar sakta hai.
Process Life Cycle
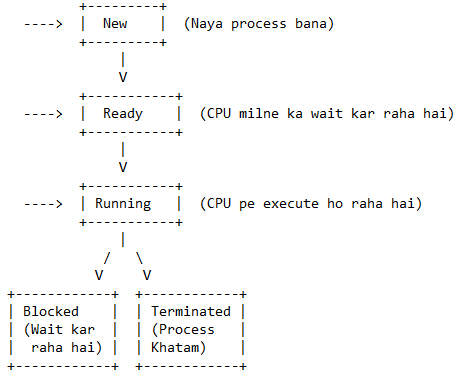
Process ki States ka Explanation:
New – Jab ek process create hota hai, par abhi execute nahi hua hai.
Ready – Process memory me load ho chuka hai aur CPU milne ka wait kar raha hai.
Running – Process CPU pe execute ho raha hai.
Blocked – Process kisi I/O operation (jaise user input ya printing) ke liye wait kar raha hai.
Terminated – Process apna kaam complete kar chuka hai aur system se remove ho raha hai.
Process Control Block (PCB) kya hota hai?
PCB ek data structure hai jo har process ki information store karta hai.
Jab bhi ek process create hota hai, OS uske liye ek PCB allocate karta hai.
PCB me kya-kya hota hai?
| PCB Field | Description |
|---|---|
| Process ID | Process ka unique number |
| Process State | Process kis state me hai (Ready, Running, Blocked, etc.) |
| Program Counter | Next instruction ka address |
| CPU Registers | CPU ke registers jo process ki information rakhte hain |
| Memory Management Info | Process ke memory allocation ki details |
| Accounting Information | CPU usage, execution time, etc. |
| I/O Status Information | Kaunse I/O devices use ho rahe hain |
PCB ka Example (Process Table Entry):
| Process ID | State | PC | CPU Registers | Memory Address | I/O Info |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 101 | Ready | 205 | … | 0xA1F4 | Keyboard |
| 102 | Running | 412 | … | 0xB2D5 | Printer |
| 103 | Blocked | 310 | … | 0xC3E6 | Hard Disk |
PCB kaha store hota hai?
PCB OS ke kernel space me store hota hai, aur OS ise process management ke liye use karta hai.
Context Switching kya hota hai?
Context Switching tab hota hai jab CPU ek process se dusre process pe switch karta hai.
Example:
1. Process A execute ho raha tha, par ek interrupt aagaya.
2. OS Process A ka PCB save karta hai.
3. OS Process B ka PCB load karta hai aur usko CPU control de deta hai.
4. Jab Process A wapas execute hoga, to OS uska PCB wapas load karega.
Multitasking ko support karne ke liye Context Switching zaroori hota hai!
Summary
Process ek running program hota hai.
Process ki states – New, Ready, Running, Blocked, Terminated.
PCB ek table hai jo har process ki details rakhta hai.
Context Switching se CPU ek process se dusre process pe switch karta hai.